




We are an SEO & marketing agency that helps brands thrive in the digital age
Helium SEO is a Digital Marketing agency that specializes in SEO, Search Ads, and Meta Ads. Maybe this sounds familiar: your company/current agency struggles to report the exact value of a campaign, your point of contact barely knows digital marketing. You see all this buzz about AI and you don’t have an agency partner that can help you implement and navigate the incredibly fast-paced world of artificial intelligence.
At Helium SEO, we wanted to make an agency that solves our client’s pain points. That’s why our SEO point of contact position is a Digital Strategy Consultant that has in-depth expertise in SEO, Facebook/Instagram Ads, and Search Ads. We developed several proprietary AI tools designed to decrease content campaign cost by up to 80%.

Hear what our clients say.
See the results for yourself
Beacon Orthopaedics
697% Increase in Keywords
Over the span of sixteen months, Beacon’s keywords increased by 697% and their organic site traffic increased over 400%.
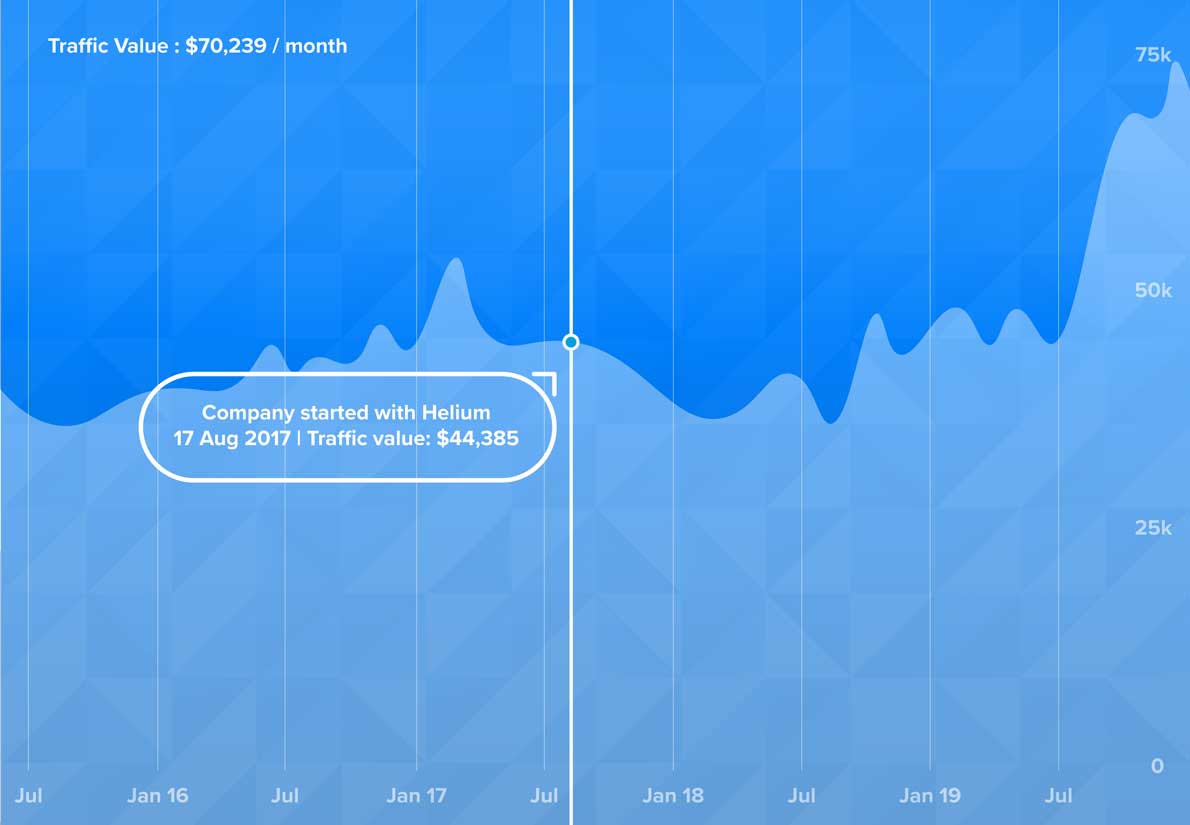
Sell Your Mac
216% Increase in Organic Traffic
Increased value of organic visitors from $44,047 to $70,239. We helped increase their organic traffic from 18,471 visitors/month to 40,052 visitors/month.
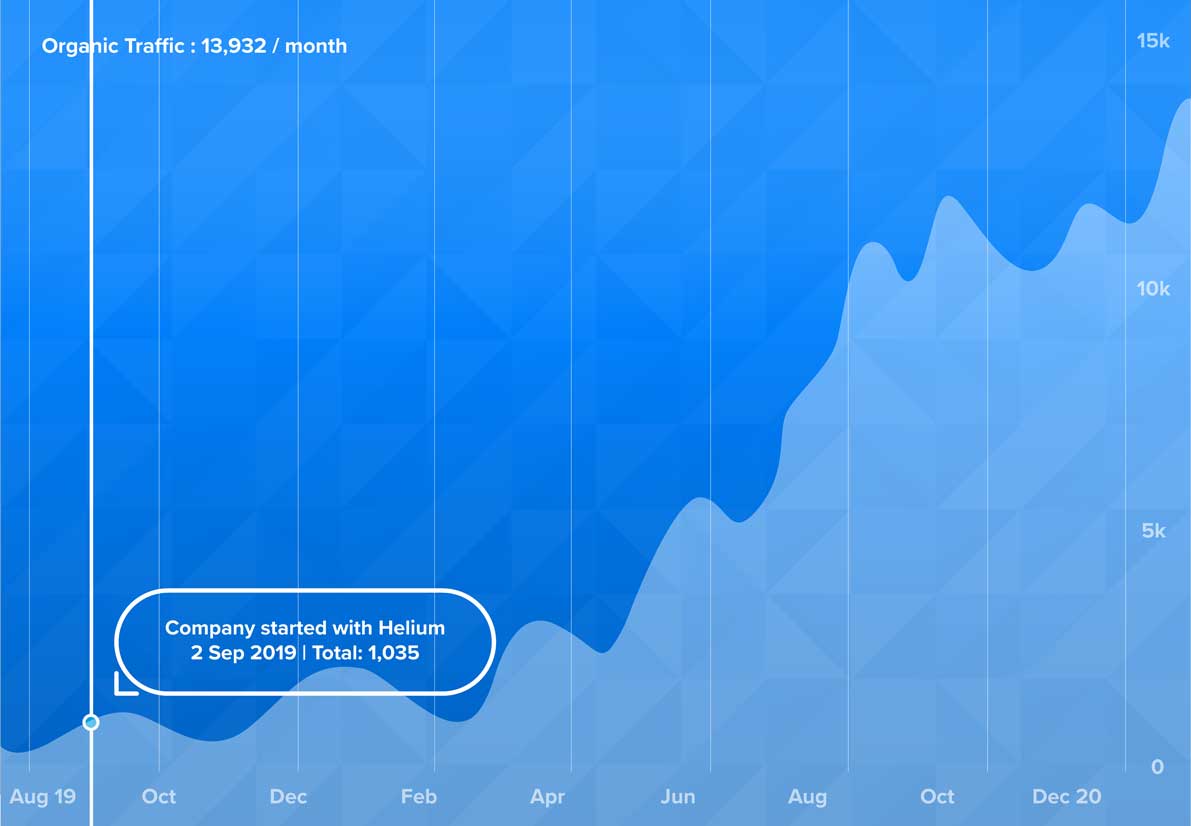
RvnGo
Ranked over 1,000 Keywords on Page 1
We helped increase unique visitors from 1,035 visitors/month to 13,392 visitors/month. Our team increased keywords ranking on page 1 from 19 to 1,111.
Our Services
Search Engine Optimization
- Technical SEO
- Market Share and SEO ROI Analysis
- Link Building
- Local SEO
- Keyword Research
- Competitor Research
- Ecommerce SEO, SaaS SEO, Healthcare SEO
AI Content Campaigns
- Outline Generation
- Article Writing
- Mass Page Campaigns
- OnPage Optimizations
- Programmatic Entity Optimization
- Internal Linking
Analytics, Reporting, and Data
- 800m Record database
- Looker Studio In-Depth Report (weekly/Monthly)
- Multi-Touch Attribution Dashboard
- Project Management Dashboard
- Helium’s Proprietary Content Campaign Dashboard
PPC: Search and Social
- Bing
- Multi-touch Attribution
- A/B tests
- We can work with you're existing creative or assist your company in creative asset generation
Get a Free SEO and Ads Audit ($1,500 Value)
Before we work together, we would like to review your marketing so we can provide you with insights to help you evaluate your current marketing campaign performance. Why is it free? It’s important to build a foundation of trust when partnering with someone, and our free ads audit is one way to built trust.
You have nothing to lose. Schedule a call with one of our PPC experts.
Get help solving your biggest marketing problems
Why has/did our SEO campaign fail at providing results?
How do I convert SEO leads?
We don’t know the ROI for SEO.
We don’t know our ideal buyers (customer persona).
We need a defined strategy and campaign roadmap.
Does AI and Bing/Google SERP changes affect SEO campaigns?
Does AI and Bing/Google SERP changes affect SEO campaigns?
Try Our Market Analysis and SEO ROI Report!
Business owners and C-suite executives need data to make educated decisions on where and how to spend their marketing dollars. Unfortunately, most businesses hear from their SEO agency that “it’s impossible to project the time it takes to rank” and “its impossible to estimate the total cost to rank”.
At Helium SEO, we believe that every decision should be backed by data, which is why we highly recommend our paid SEO viability audit. In the audit, we tell you how many articles you’ll need to write, the likely MRR/ROI, the amount of backlinks you’ll need, and you’ll know the days and dollars required to make your goals happen. Lastly, you’ll get a snapshot of the organic competition and you’ll see how many articles and backlinks they have for their keyword clusters. If you’ve got big goals, you should start here.


Get to know us
Meet the Helium team for your SEO campaign
We’re focused on delivering revenue first to a variety of industries nationwide. Inc. 5000 named us one of the fastest growing companies in the country, and that growth is directly tied to the results we deliver to businesses like yours.
At Helium SEO, we believe that clients should communicate with industry experts instead, which is why all of our points of contact are absolute SEO Pros.
What our clients are saying...
We have driven our brand SellYourMac.com to the top of Google for almost every keyword we track... if you Google "sell mac", "Sell macbook", "sell my mac", "where to sell my mac", etc we are literally #1 and I have Helium to thank! I plan to continue to expand our SEO services with their excellent team to continue to boost traffic, clicks, and revenues across SellYourMac.com.
FAQs about Search Engine Optimization
How long does it take to generate results?
Generating SEO results typically takes about 4 to 6 months. However, significant improvements may take up to one year or even longer. The speed at which you see results is dependent on numerous factors such as your website’s age, its current state, the amount of content, and the competitiveness within your industry. Remember that SEO is a long-term strategy and requires continuous effort.
How do you predict the length of time and the cost of an SEO campaign?
Predicting the length of time and cost of an SEO campaign can be complex as there are a plethora of factors that contribute to these elements. Here’s a basic manner to estimate:
1. Scrutinize the website: Assessment of the website is crucial. It includes understanding the structure, content, link portfolio, and keyword density. You should also review the website’s technical aspects like its loading speed, URL structure, and mobile optimization.
2. Define the Goals: The scope of your SEO campaign greatly depends on what you want to achieve. Goals can range from improving domain authority to boosting organic traffic or pushing a specific set of keywords in top rankings.
3. Keyword Research: Research is vital to understand how your targeted keywords are ranking. If they’re ranking on the second or third page of SERPs, it may take less time and cost to push them further. But if they’re nowhere in sight, then it might take more time and cost.
4. Competitive Analysis: Understanding what your competitors are doing is also important. If you’re competing with highly authoritative sites, time and effort will increase.
5. Create a Strategy: Based on the above factors, create a strategy that includes on-page optimization, content creation, link-building etc., and estimate the time each of these
Is there a discount for combining SEO and PPC?
Yes, Helium SEO can discuss offering a discount when combining these services.
Does Helium SEO offer Web Design?
Yes Helium does. Please contact us to get more details.
What is the difference between National SEO campaigns and Local SEO campaigns?
National SEO campaigns target a broader, nationwide audience. They are used by businesses that offer products or services across an entire nation or even internationally. These campaigns focus on ranking for broad keyword terms and do not necessarily focus on a specific geographical area.
On the other hand, Local SEO campaigns target a specific geographical area such as a city, state, or region. This strategy is helpful for local businesses that want to attract customers in their immediate area. Local SEO campaigns focus on geographical keyword terms and also aim to increase visibility on local listing sites and directories.
Why is content important for SEO?
Content is crucial for SEO for several reasons:
1. Relevant and Quality Content Attracts Search Engines: Search engines are designed to provide users with the most relevant results. High-quality, relevant content is likely to get a higher ranking on search engine results pages, leading to increased visibility and traffic.
2. Keywords Usage: Quality content allows businesses to incorporate keywords that consumers use to search for the products or services they offer. This helps search engines to index the website appropriately and improve its ranking.
3. Increased User Engagement: High-quality content is likely to resonate more with users, keeping them engaged longer. The more time users spend on a webpage, the more search engines consider the site to be valuable, leading to improved rankings.
4. Backlinking: If your content is high quality and valuable, other websites are more likely to link to it, improving your backlink profile. Backlinks are a crucial component of SEO as they signify credibility and relevance to search engines.
5. Improved User Experience: Quality content enhances the user experience, as it provides users with the information they are looking for. A positive user experience can lead to higher conversion rates, repeat visits, and positive reviews/social shares– all signals that search engines recognize and reward with improved ranking positions.
Why are backlinks important for SEO?
Backlinks are important for SEO for several reasons:
1. Improved Organic Ranking: Backlinks help in better search engine rankings. When your content gets linked to other sites, it improves your chances of ranking higher in search results.
2. Faster Indexing: Backlinks help search engine bots discover links to your site and index your website faster.
3. Referral Traffic: One of the major benefits of backlinks is that they help get referral traffic. Usually, referral traffic is targeted and has a low bounce rate.
4. Builds Your Authority: Backlinks from authoritative, relevant, and well-respected websites can increase the authority of your website in the eye of search engines.
5. Increases Brand Visibility: The more backlinks you have, the more your brand is visible online.
6. Builds Network: Backlinks not only bring traffic but can also serve as a networking tool. It can help you build relationships with key people in your industry which can be very beneficial.
Remember healthy and search-engine-approved link-building strategies are key. Creating spammy or unnatural ways of building backlinks may harm your site’s reputation and SEO.
What are the most important local SEO ranking factors?
1. Google My Business Listing: This is a key factor for improving your ranking on local searches. It provides Google with accurate information about your business such as location, business category, hours of operation, etc.
2. Online Reviews: Google takes into account the number and the quality of reviews on your Google My Business listing. Reviews show that your business is legitimate and provides value to customers.
3. NAP Consistency: NAP (Name, Address, Phone number) must be consistent across all platforms that contain information about your business, like directories, website, and social media profiles.
4. Local Keywords: Including local keywords on your website is critical for appearing in local search results. Google uses these keywords to understand what your business offers and where it’s located.
5. Mobile-Friendly Website: With the increase in mobile searches, having a mobile-friendly website affects ranking. Google prefers websites that are mobile-friendly, providing a good user experience.
6. High-Quality Backlinks: Backlinks act as a vote of confidence from other websites. The more high-quality local backlinks you have, the more credible your business appears to Google.
7. Website Loading Speed: Google takes website loading speed into account when ranking web pages. The faster your website loads, the better.
Schedule a free consultation with one of our digital sales consultants
We want to add your business to the list of partner companies that made millions through a partnership with Helium.




We are a digital marketing agency building SEO campaigns and solutions to help brands achieve their goals and generate revenue. Locations we serve.






